The 5 Areas That Define Your Organizational Change Capability

3 Mins
Updated: August 7, 2024
Published: May 26, 2021

Building an enterprise change capability is a rewarding journey that yields strong returns for organizations, but the journey is not without challenges. One of the biggest problems leaders face is with measuring the organization's progress toward change management maturity goals. Prosci addresses this issue with a research-based, practical solution.
Prosci Change Management Maturity Model
Based on more than two decades of research, the Prosci Change Management Maturity Model serves as a measuring stick for an organizational change management progress. Informed by the five areas that define change capability within an organization, the Change Management Maturity Model framework enables you to rate your strengths and weaknesses, and then use the scores to drive targeted improvements that will grow your maturity level in the right areas.
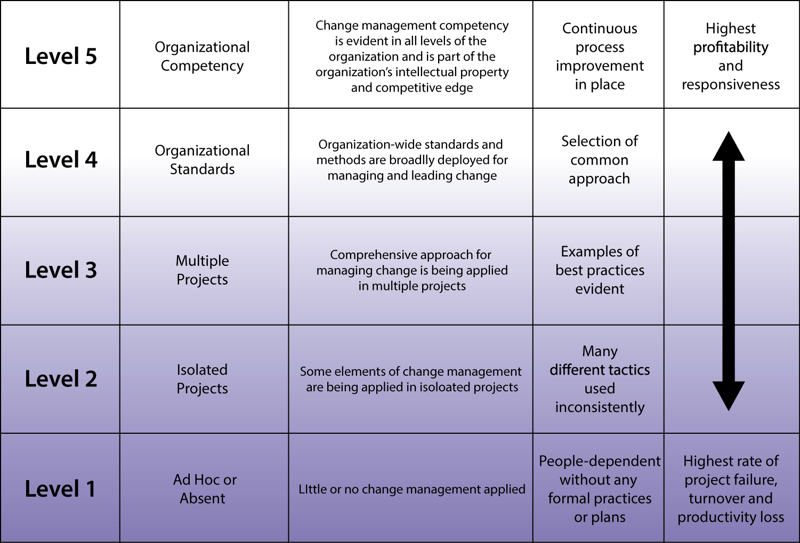
The Prosci Change Management Maturity Model
Note that the five levels in the maturity model above are the potential outcomes your organization can achieve when growing enterprise change management capability. The levels are sequential, cumulative and incremental, and progress varies by organization. For example, your organization might be at level 1.2 today and be working toward a desired future state of 3.9 within three years, while a smaller organization may need a longer timeline to close a similar gap.
But before you identify a future state and plan for the transition state, your organization must determine your current state of change management maturity. To accomplish this, you assess your organization in terms of the five capability areas that define change management maturity. These are Leadership, Application, Competencies, Standardization and Socialization. Let's look at some examples of each area below.
Capability area 1: leadership
 This capability area is not about leadership in general. It's about senior leadership support for change management capability.
This capability area is not about leadership in general. It's about senior leadership support for change management capability.
Such leadership exists in multiple forms, including:
- Primary sponsor for change management deployment
- Sponsor coalition for deployment
- Communications from key leaders about the importance of change management
- Vision for the organizational change management capability
- Business rules, policies and procedures making change management a requirement
- Funding and resources for the change management capability project
- Leadership accessibility, decision making, and engagement with the project team working to deploy change management
Questions to ask:
- How committed is leadership to organizational change management?
- What activities or messages is the leadership undertaking to communicate the value of change management and the effort to build an internal competency?
- Who is sponsoring change management deployment?
If your organization scores low in the Leadership capability area, you should focus on this area first when building an organizational change capability.
Capability area 2: application
 An organization that is mature in change management will apply a change management methodology and tools on projects and initiatives throughout the organization.
An organization that is mature in change management will apply a change management methodology and tools on projects and initiatives throughout the organization.
Examples from the Application capability area include:
- A large percentage of projects applying change management
- Multiple parts of the organization (e.g., divisions, functions, units) applying change management
- Easily accessible tools for managing change
- Dedicated time and resources available to apply change management on projects
When evaluating this area, remember to consider:
- Consistent change management methodology and tools
- Types of projects applying change management
- Change management practitioner availability for applying processes and tools on projects
- Budget and funding availability for change management on projects and initiatives
Capability area 3: competencies
 Change management is ultimately implemented by employees, people managers, leaders, project teams and practitioners throughout the organization. The third capability area, Competencies, looks at the training and development of key roles and groups that must apply change management tools and principles.
Change management is ultimately implemented by employees, people managers, leaders, project teams and practitioners throughout the organization. The third capability area, Competencies, looks at the training and development of key roles and groups that must apply change management tools and principles.
Evaluate whether and to what extent your organization has:
- Equipped and trained change management practitioners
- Delivered executive and senior leader training on change management and sponsorship
- Delivered training to people managers on coaching employees through change
- Trained employees on guiding themselves through change
- Delivered project team training on change management
- Demonstrated effectiveness of training programs for change management
- Offered continuing education opportunities in change management
In addition to understanding who has been trained, be sure to understand whether these individuals have demonstrated competency in their change management roles.
Capability area 4: standardization
 Standardization looks at the mechanisms and systems that can be used to institutionalize change management. By moving toward common and consistent application of a standard organizational approach, you increase the effectiveness of change management and create a common language around change.
Standardization looks at the mechanisms and systems that can be used to institutionalize change management. By moving toward common and consistent application of a standard organizational approach, you increase the effectiveness of change management and create a common language around change.
Examples of Standardization include:
- Adoption of a standard approach and methodology
- Provision of standard tools
- Establishment of complete change management training curriculum
- Structural elements (e.g., functional group, community of practice, networks)
- Integration with standard project delivery process
- Embedded change management in ongoing improvement systems
- Integration with "change-initiating" processes and systems (e.g., Six Sigma, strategic planning)
Standardization enables effective change management to become an integral component of the way the organization introduces changes. It's important to think strategically about what will most successfully embed change management into your organization’s processes and structure.
Capability area 5: socialization
 The fifth and final capability area, Socialization, focuses on building commitment and buy-in for change management at every level of the organization. Socialization includes understanding, appreciation and acknowledgement of the need to apply change management to change projects and initiatives in the organization.
The fifth and final capability area, Socialization, focuses on building commitment and buy-in for change management at every level of the organization. Socialization includes understanding, appreciation and acknowledgement of the need to apply change management to change projects and initiatives in the organization.
An organization with mature levels of Socialization should or may have:
- An executive charter for building change management capability
- Understanding of the value of change management
- Buy-in and support for applying change management
- A common and shared definition of change management
- Reinforcement for sustained change management application
- Cultural values related to managing the people side of change
- Evaluation of change management effectiveness
Measure Change Management Maturity
By measuring these five capability areas, you can begin to understand where your organization stands in terms of organizational change management capability. In addition to documenting your current level of maturity, we also recommend establishing a measure for your desired future state. With the current state and desired future state clearly defined, you can then build a roadmap to close the gap.