The What, Why, Who and How of Change Management

4 Mins
Updated: July 11, 2025
Published: September 1, 2021

Do you want to engage organizational leaders and increase their understanding of change management in a matter of minutes? This overview provides the foundation they need—the what, why, who and how of change management—so you can quickly explain the benefits your organization can achieve by focusing on the people side of change.
What Is Change Management?
Change management is the application of a structured process and set of tools for leading the people side of change to achieve a desired outcome. Change management is also:
- A process used to manage system, process and organizational changes
- A leadership competency for enabling change within an organization
- A strategic capability designed to increase change capacity and responsiveness
Why Is Change Management Necessary?
Prosci’s Best Practices in Change Management benchmarking data shows that initiatives with excellent change management are seven times more likely to meet objectives than those with poor change management. And it’s not necessary to achieve excellence to see improvements in meeting objectives. For example, increasing change management effectiveness from “poor” to “fair,” increases the likelihood of meeting objectives threefold.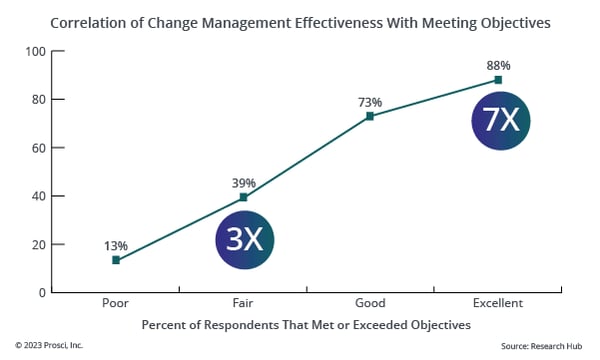
Effect on adoption and usage
Applying change management can directly impact adoption and usage. Specifically, it can affect:
- Speed of adoption – How quickly are people up and running on the new systems, processes or job roles?
- Utilization rate –How many people (of the total population) are adopting and using the new solution?
- Proficiency – How well are individuals performing compared to the level expected in the design of the change?
Effect on project objectives and ROI
When change management delivers targeted levels of adoption and usage, the probability of achieving business objectives on time and on budget increases. When the people side of change is poorly managed, projects fall behind schedule, fewer people engage in the change, and proficiency levels drop. Ultimately, projects deliver a lower ROI or, in some cases, fail completely.
Who Is Involved in
Successful Change Management?
The roles you need for successful change can vary according to project size and scope. The core roles in change management are:
Sponsors
Change management sponsors give credibility and authority to the change. Primary sponsors, sponsors, and sponsor coalitions have distinct yet overlapping responsibilities:
The primary sponsor authorizes the change and is ultimately accountable for ensuring the desired outcomes of the change are realized for the organization. The level of sponsorship required is determined by the risk level of the change. For example, the primary sponsor for a high-risk change should be a senior executive or officer of the organization.
During change, a primary sponsor's role is to fulfill the ABCs of Sponsorship: Active and visible participation throughout the project, Build a coalition of sponsorship with peers and managers, and Communicate directly with impacted individuals and groups.
Additional sponsors are typically required for changes that impact multiple groups in an organization. Such sponsors may be senior managers with responsibility for individuals or systems impacted by the change, or influence leaders whose active involvement is necessary to achieve successful change outcomes for certain groups.
The sponsor coalition is a group of sponsors who support the successful implementation of a specific change throughout the organization by fulfilling the ABCs of Sponsorship with the impacted groups in their respective areas of responsibility. Having a strong sponsor coalition is a leading indicator of change success, while a weak sponsor coalition is a leading indicator that a change will fall behind schedule, miss objectives, or fail completely if the weakness is not effectively addressed.
People managers
People managers contribute to successful change outcomes by supporting direct reports in their own journeys by fulfilling five key roles: Communicator, Liaison, Advocate, Resistance Manager and Coach (CLARC). People managers are the preferred senders of change messages related to how a change impacts their direct reports personally. They are essential to convey the “What’s in it for me?” (WIIFM) messages to their teams.
Project manager
The project manager contributes to successful change outcomes by designing, developing and delivering the technical solution with individual adoption and usage in mind from the beginning. They also collaborate on a unified approach with the change practitioner.
Change practitioner
The change practitioner contributes to successful change outcomes by applying structure and intent to change, enabling and equipping other change roles, and collaborating on a unified approach with the project manager. The change practitioner develops a customized strategy and a set of change management plans, including a Sponsor Plan, People Manager Plan, Communications Plan, and Training Plan.
Impacted individual (employee)
The impacted individual contributes to successful change outcomes by participating in the change, understanding their emotional responses to change, and identifying what support they need to take control of their change experience and thrive during change.
How Does the
Change Management Process Work?
Change management occurs at individual and organizational levels.
Individual change management
Individual change management is about managing change one person at a time. Organizational change can only happen when individuals change. There are five elements or outcomes that serve as the sequential building blocks of individual change. When you ensure that all five elements are present, the individual is able to adopt and use the change. The Prosci ADKAR Model defines the five outcomes an individual needs to achieve for a change to be successful:

The ADKAR Model is used to guide individuals through a particular change and address any roadblocks or barrier points encountered along the way.
Organizational change management
Although all change happens one person at a time, organizations manage those individual transitions collectively. Organizational change management involves designing and implementing change management activities to enable impacted individuals and groups to adopt and use changes.
The organizational change management process is the critical link between individual change and organizational change. The Prosci 3-Phase Process is a structured and repeatable approach to enable the people side of change to achieve change success and deliver value to the organization. Each phase includes a set of plain language questions to be answered for a specific change and a deliverable that documents the completion of the phase.
Prosci 3-Phase Process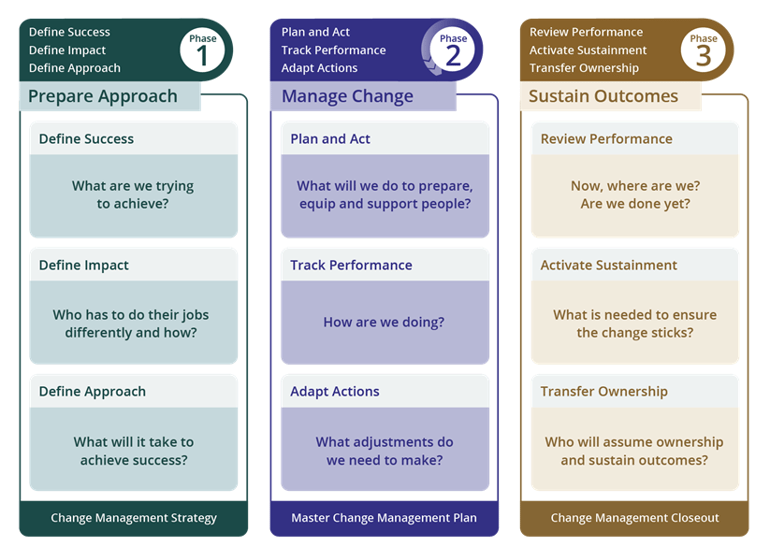
Enterprise change management
Enterprise change management is the structured and intentional deployment of change management across and throughout an organization. The deployment goes beyond applying effective organizational change management to all change initiatives. By institutionalizing change management practices, processes, capabilities and competencies across the organization, applying change management becomes the norm, part of the organization's values, and part of your organizational DNA. When enterprise change management is done well, being able to anticipate and effectively implement change becomes a core competency and a source of strategic advantage.
Benefits of Change Management
Given the volume and complexity of changes today, it can be easy for change practitioners to see the benefits of effective change management. You see firsthand how it greatly increases the likelihood of successful outcomes, enables you to capture the people-dependent portion of project ROI, helps you mitigate employee resistance, and much more. By sharing the “what, why, who and how" of change management with busy leaders, you give them the information they need to understand change management quickly, so you can maximize their time and yours, and start elevating change success in your organization together.



