Use the ADKAR Model for Change Success

8 Mins
Updated: April 18, 2025
Published: November 1, 2024

Managing change successfully is essential for organizations everywhere. If change isn’t managed responsibly, it can impact everything from employee engagement and retention to project success rates and ROI. The good news is that applying the Prosci ADKAR® Model provides structure and flexibility when implementing change.
As a result, organizations can deliver strong results and outcomes from virtually any change.
But how exactly does the ADKAR Model work?
This article examines how our ADKAR Model guides organizations through critical changes.
What Is the ADKAR Model?
The Prosci ADKAR Model is a framework for managing individual change in an organization. It’s based on the premise that organizational change starts when individuals change. This model guides individuals through a particular change, addressing roadblocks along the way.
ADKAR is a core part of the Prosci Methodology—a structured, adaptable and repeatable approach for managing the people side of change. It enables organizations to continually change and evolve to succeed.
Here's how the Prosci Methodology, and some of its models and frameworks, work together:
1. Prosci ADKAR Model – This model puts people at the center of change. ADKAR describes the five building blocks necessary for individual change: Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability and Reinforcement. Our ADKAR Model guides individuals through the change process and helps them move past common barriers that create resistance to change.
2. Prosci Change Triangle (PCT) Model – The PCT Model highlights four critical aspects of successful organizational change efforts—leadership/sponsorship, project management, change management and success—and how they work together.
3. Prosci 3-Phase Process – This step-by-step framework enables you to deploy the entire change management process in three phases:
- Phase 1 – Prepare Approach involves defining success and developing a change management strategy that aligns with it.
- Phase 2 – Manage Change involves creating and implementing change management plans and tasks successfully.
- Phase 3 – Sustain Outcomes – involves ensuring that changes are adopted and sustained for the long term.
4. Change Management Plans – These can include specific plans such as the Sponsor Plan, People Manager Plan, Communications Plan, Training Plan, Resistance Management Plan, and others—each addressing critical aspects of the change management strategy.
5. Role Roster – This identifies the specific roles needed to successfully manage the change initiative from an employee-centric perspective.
6. Unified Value Proposition (UVP) – This visual framework illustrates how change management and project management are complementary disciplines with a common objective of achieving success.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the components of the Prosci ADKAR Model.
Prosci ADKAR Model

Awareness
Here’s how to increase Awareness:
- Ensure team members understand the need for change – Answer the “why” of the change by outlining the reason it’s necessary. Consider an improvement in electronic medical records (EMR) as an example. Healthcare providers might resist this change initially, querying whether it’s necessary and how it could impact their ability to give care. When you explain how the system enables the sharing of patient records across departments (like acute care, rehabilitation, and home care providers), it immediately shows why the solution is necessary: to improve patient care.
- Explain the downsides of not implementing the change – Show employees what will happen if the change isn’t implemented. For example, in financial services, not complying with federal or state regulations can have significant consequences like costly fines and rework. Ultimately, noncompliance with a regulatory change creates a reactive cycle that monopolizes leaders and harms the institution's reputation.
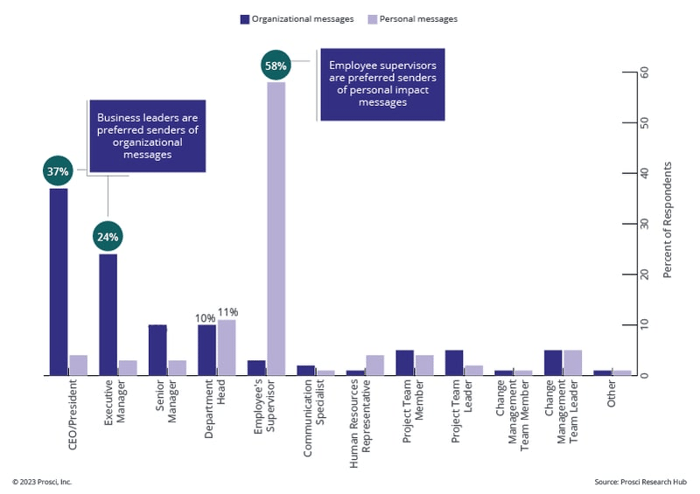
- Use the right people to share key messages – Ensure the right people share the right messages when building awareness of the need for change. Prosci research shows that people prefer to receive personal-impact messages from supervisors but would like organizational messages to come from business leaders.
- Provide the right training and support – Give employees the training, resources and support they need to understand the impact of change at an individual level. If you consider a change involving an ERP systems implementation, this would involve showing end users like the accounting team how the new system works, how it impacts their day-to-day, and how they can use it effectively.
Preferred Senders of Messages
Desire
Once people understand why a change is necessary, the next step is to make a compelling case for adopting the change. The aim is to increase the Desire element, enabling team members to participate in the change and move forward through their transitions.
Here are some ways to increase Desire:
- Answer WIIFM – Team members may ask, “What's in it for me (WIIFM)?” With our ERP systems example, team members would need to hear how the new system will save them time, pay vendor invoices faster, and eliminate frustrating bottlenecks in their processes.
- Share case studies – Show team members where change has made an impact to support the concept and provide evidence to back up your claims. For example, you might show how other banking institutions have upgraded their regulatory compliance process, reduced MRAs and fines, and improved relationships with regulators.
Knowledge
Provide training and support for team members to develop their knowledge and confidence around the change. This involves showing them what to do during the transition and how to perform effectively in the future state.
Let’s walk through some of the ways to develop knowledge:
- Explain how individuals will make the change – Communicate with team members about what the change involves and how it will impact them individually. Change looks different for everyone, and it’s important to provide unique training and resources to suit each individual or similarly impacted group. For example, front-line workers on a manufacturing floor will experience change differently from admins working in the in-plant office.
- Identify skill gaps – Identify where employees need new skills and training to incorporate the change. Talk to employees about their current abilities, review HR documentation, and narrow down the key skillsets that you’ll need refine before the change goes live. Then, provide hands-on instruction and interactive training to give people the skills to enact change.
- Train in a safe environment – Be sure that any training is held in a safe environment to ensure that customer data and privacy aren't compromised. In our patient record example, ability building should happen away from patients to keep their data safe and secure until team members are confident in using the system accurately.
Note that it's a common mistake for organizations to start the change journey with training, effectively skipping Awareness and Desire. But those arriving at training without Awareness and Desire are unlikely to have a learning mindset. Before training, you must ensure that team members understand why the change is happening and have decided to engage with the change. Team members must want to learn for the change to be successful.
Ability
Ability is the stage where the change becomes clear in behaviors, mindsets and other expected outcomes. These successful outcomes are defined at the start of a change. For example, if the change involves a new shift scheduling system, success would be achieved by team members using the system effectively.
Here are two ways to increase Ability:
- Provide hands-on practice during training – Give team members a chance to implement their training by practicing it as part of the training process. For example, if you’re rolling out a new CRM system, let everyone try it to ensure they understand how it works.
- Offer expert resources to help team members – Ensure that all team members have access to any resources or expert advice needed to perform the change successfully. For example, in manufacturing, offer training documentation or mentorships from other machine operators or engineering experts.
Reinforcement
As human beings, we tend to slip back into past, comfortable patterns without realizing it. Plus, it can be hard to keep changes in place in larger organizations, where multiple people are involved in the change process.
Reinforcement is about maintaining change over time, preventing things from reverting to the old ways.
Here’s how to increase Reinforcement:
- Monitor progress – Define success measures that clearly indicate if the change is happening. You can create many metrics to measure success—such as the waiting time to transfer patients to rehabilitation, setup time for a manufacturing production line change, and reductions in data privacy breaches. Tracking metrics ensures that change stays on course to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Engage senior leaders – Active and visible support from leaders can significantly impact its long-term success. Leaders must endorse change as an integral part of the organization to encourage team members to follow it through.
How Effective Is the ADKAR Model?
Let’s explore how using the ADKAR change management model guides organizations through critical changes with a few practical examples.
Rolling out a healthcare policy change
ADKAR helps healthcare facilities successfully roll out new policies, helping to ensure that team members understand the need for new policies and how the change will directly impact patient care.

Let’s use a handwashing policy as an example:
- Awareness – Communicate the need for the handwashing update, explaining that it will improve patient care by reducing the spread of contagions and contaminants.
- Desire – Highlight case studies showcasing the reduction of infections and illnesses in facilities where this new policy was implemented.
- Knowledge – Teach people about the new policy through demonstration, practice, and informative posters at handwashing stations.
- Ability – Provide expert support to team members, giving feedback to team members as the new habits are built.
- Reinforcement – Showcase the positive results periodically after the change has begun.
Ensuring regulatory compliance in financial services
The ADKAR Model helps financial institutions comply with complex regulatory changes, ensuring the likelihood of adoption.
- Awareness – Explain the regulatory requirements and the potential impacts on the institution, as well as the risks of noncompliance, resulting in financial penalties and reputational damage. Have leaders communicate the urgency and importance of the change to reinforce its significance.
- Desire – Foster a willingness among employees to support and participate in the change. Address concerns by conducting Q&A sessions for employees, and offer incentives such as recognition programs for successfully adopting new regulations.
- Knowledge – Provide employees with training and information to understand how to comply with the new regulations, including the specifics of the regulatory changes and how they'll be implemented.
- Ability – Enable employees to implement the required skills and behaviors for compliance through hands-on practice like role playing. Ensure that managers and team leaders are equipped to help employees as they navigate the new requirements.
- Reinforcement – Sustain the change and ensure ongoing compliance through regular check-ins, and recognize teams that who demonstrate exemplary compliance behavior.

Launching new staffing models
Applying the ADKAR Model can be a beneficial method for launching new staffing models after organizational changes, such as a merger.
Here’s how it ensures everyone follows a structured approach to creating a cohesive and collaborative organizational culture:
- Awareness – Explain why the merger is happening, focusing on the expected benefits.
- Desire – Highlight the benefits of the new structure to team members, including complementary skills that lead to opportunities for career growth and improved teamwork.
- Knowledge – Teach team members about the behaviors they need to demonstrate to help the new structure succeed. Cover who they’ll work with going forward, offer means for team building, and teach people leaders how to show up for their new teams.
- Ability – Help team leaders put the change into practice by helping their teams adopt and demonstrate required behaviors. Ensure team members apply the team-building activities and behaviors to convert them into habits.
- Reinforcement – Use team member feedback surveys to track progress and identify corrective actions where teams aren’t flourishing. Use a 360-degree feedback system to reinforce the new ways of working.
Implementing new technologies
New technologies are becoming more prevalent in organizations. But launching a new system can be difficult. For example, losing key data or being unable to access certain information will create operational challenges and resistance behaviors that hold successful changes back.
Here’s how the Prosci ADKAR Model can help you overcome these challenges and implement new technology:
- Awareness – Communicate the rationale for implementing new technology, such as increased efficiency or compliance with new regulations.
- Desire – Generate enthusiasm by highlighting the benefits of new technology, including how it will make their lives easier and improve processes.
- Knowledge – Train and coach staff on using the new technology for a hands-on approach, increasing their understanding of the system.
- Ability – Give team members access to virtual support and documentation to aid their learning and ensure they’re confident using the new technology.
- Reinforcement – Track usage to ensure team members use the new system. Depending on the new technology, you could track other change management metrics like proficiency and speed of adoption.
Why Is Change Management Important for Organizations?
Take a look at why an effective change management process is vital for almost every industry, from healthcare and financial services to IT and manufacturing.
Adapting to constant change
Organizations face ongoing internal and external pressures, such as technological advancements, market competition, and evolving customer expectations. Effective change management helps organizations navigate these shifts by providing a structured approach to successfully implementing changes.
A structured change management model also ensures that leaders and employees at all levels are equipped to adapt to changes. Using the Prosci ADKAR Model shows how change happens, putting the spotlight on the steps we go through as we adapt to new ways of working. From front-line workers to senior leaders, everyone learns how change happens and where to focus their energy during each part of the journey.
The more we understand how to change, the quicker and easier it can be for people to adapt. Plus, change management enables employees to continue doing their jobs as effectively as possible during changes—with minimal disruption, less stress and burnout, and better employee engagement.
Organizations also benefit from change management in terms of project results. Prosci research shows that projects with effective change management are more likely to achieve significantly higher levels of success.
Correlation of Change Management and Success
.png?width=614&height=200&name=7X%20more%20likely%20circles-2023%20(1).png)
Our flexible and adaptable ADKAR Model can be applied to many types of changes. Explore our customer case studies to learn more about the ADKAR Model and Prosci Methodology and how organizations apply them to achieve remarkable results on projects and initiatives,
Work With Prosci To Implement Successful Organizational Change
Putting people at the heart of change is crucial to success, which is why ADKAR is incredibly valuable for organizations looking to implement change. When you make people your focus, you will be more successful at encouraging employees to engage, adopt and use new processes, tools or techniques. In fact, research and experience consistently shows that using our ADKAR Model to drive change improves the likelihood of your success with changes of all kinds.